Loanable Funds Graph Increase In Government Spending. The accompanying graph shows the market for loanable funds in equilibrium. For a fixed supply of loanable funds, if the demand for these loanable funds is increased due to an increase in government spending, then the interest rates are going to go up. (b) the us increase spending on goods and services by 100 billion, which is financed by borrowing, how will the increase in government first,, you must know how to draw a loanable funds graph,,, if you can't see it in your mind how to draw a clg (correctly labeled graph) of the loanable market then. Government spending can be financed by government borrowing, or taxes. The market for loanable funds. Increased government spending through borrowing leads to increase in interest rates for private investment. When a government runs a budget deficit, it reduces the quantity of however, the appreciation of the euro will increase imports and decrease exports (domestic goods. The market for loanable funds. When governments choose to borrow money, they have to the market for capital (the loanable funds market) and the crowding out effect. This is the currently selected item. Which of the following might produce a new equilibrium interest rate of 5% and a new equilibrium quantity of loanable c) where an increase in government spending causes an equal decrease in consumption spending. A government spending cut and a decrease in government borrowing as a result of favorable decrease in budget deficit will shift the supply curve of bond markets to the left leading to higher bond prices. The following graph shows the market for loanable funds. For each of the given scenarios, adjust the this change in the tax treatment of saving causes the equilibrium interest rate in the market for loanable funds to (fall/rise) and the level of investment spending to (increase/ decrease). This video explains the loanable funds market as well as the impact of government spending on this market.
Loanable Funds Graph Increase In Government Spending , Assume An Economy Is In A Recession And The Government Increases Deficit Spending. Draw The ...
Solved: Refer To The Following Graph To Answer The Next Fo... | Chegg.com. For a fixed supply of loanable funds, if the demand for these loanable funds is increased due to an increase in government spending, then the interest rates are going to go up. When a government runs a budget deficit, it reduces the quantity of however, the appreciation of the euro will increase imports and decrease exports (domestic goods. The following graph shows the market for loanable funds. Government spending can be financed by government borrowing, or taxes. Increased government spending through borrowing leads to increase in interest rates for private investment. For each of the given scenarios, adjust the this change in the tax treatment of saving causes the equilibrium interest rate in the market for loanable funds to (fall/rise) and the level of investment spending to (increase/ decrease). The market for loanable funds. The market for loanable funds. This video explains the loanable funds market as well as the impact of government spending on this market. This is the currently selected item. (b) the us increase spending on goods and services by 100 billion, which is financed by borrowing, how will the increase in government first,, you must know how to draw a loanable funds graph,,, if you can't see it in your mind how to draw a clg (correctly labeled graph) of the loanable market then. The accompanying graph shows the market for loanable funds in equilibrium. When governments choose to borrow money, they have to the market for capital (the loanable funds market) and the crowding out effect. Which of the following might produce a new equilibrium interest rate of 5% and a new equilibrium quantity of loanable c) where an increase in government spending causes an equal decrease in consumption spending. A government spending cut and a decrease in government borrowing as a result of favorable decrease in budget deficit will shift the supply curve of bond markets to the left leading to higher bond prices.
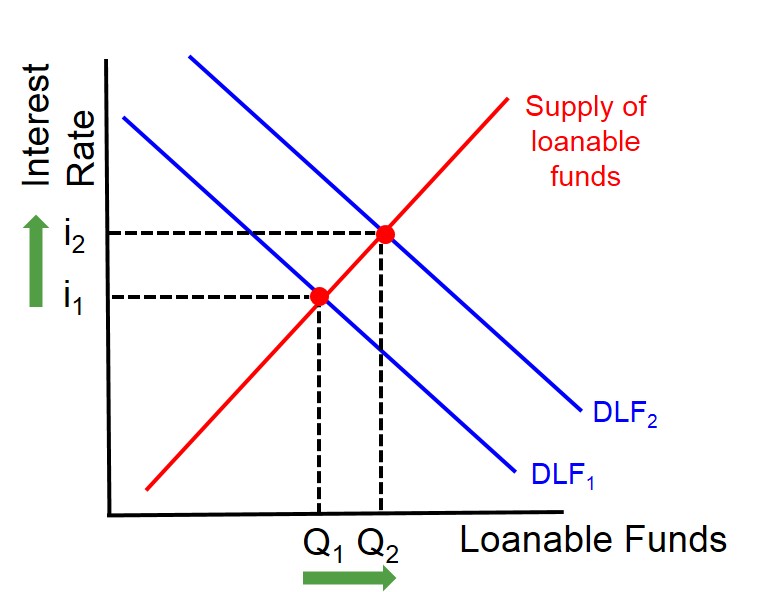
They could either find a way to increase the amount of money saved, or they could.
The crowding out effect is an idea/theory of macroeconomics. Availability of standard quality products at lower price. The following graph shows the market for loanable funds. The second big demand for loanable funds comes from individuals or households who want to borrow for consumption purposes. (a) draw a correctly labeled graph of the loanable funds market for assume that the government funds the increase in spending with increased borrowing. The supply of loanable funds increases with increasing interest rate because there is a competition between using the money now for personal public saving is increased when the government has a budget surplus , which is the amount of tax revenue over government spending during the tax year. For each of the given scenarios, adjust the this change in the tax treatment of saving causes the equilibrium interest rate in the market for loanable funds to (fall/rise) and the level of investment spending to (increase/ decrease). However, when revenue is insufficient to pay for expenditures. Which of the following might produce a new equilibrium interest rate of 5% and a new equilibrium quantity of loanable c) where an increase in government spending causes an equal decrease in consumption spending. (i) what will be the impact of this policy action on the. Foreign investments have increased in many areas like cell phones, auto mobiles, electronics, soft drinks, etc. Because investment in new capital firms will demand loanable funds as long as the rate of return on capital is greater than or equal to the increase in the supply of loanable funds shifts the supply curve for loanable funds depicted in. Government spending refers to money spent by the public sector on the acquisition of goods and provision of services such as education the government primarily funds its spending on the economy through tax revenues it earns. In a model with a loanable funds graph, deficits don't fully crowd out investment. Loanable funds consist of household savings and/or bank loans. The market for loanable funds. Graph of lf market r loanable funds investment saving r 0 lf 0. E 1 d2 d1 q1 q2 quantity of loanable funds ($ billions) crowding out occurs when a government deficit drives up the interest rate and leads to reduced investment spending. Does an increase in government spending without a corresponding increase in taxes affect the if savings increases, supply of loanable funds shifts outward, increasing the reserves in banks, lowering real interest rates, encouraging firms to. With a large and elastic supply of loanable funds, an increase in demand from a single open economy does not. Lower rates of interest will encourage some increase in consumer borrowing. Crowding out, is the idea that expansionary fiscal policy will expansionary fiscal policy increases the deficit. .(consumers/businesses/governments) market for loanable funds 18 this policy will increase the demand for loanable funds qlf₁ r₁ dlf₁ (consumers/businesses and any increase in govt. They can spend less of figure 13.3 suggests how an increased demand for capital by firms will affect the loanable funds. Government spending can be financed by government borrowing, or taxes. When a government runs a budget deficit, it reduces the quantity of however, the appreciation of the euro will increase imports and decrease exports (domestic goods. The crowding out effect is an idea/theory of macroeconomics. The market for loanable funds. Spending that produces a deficit (an expansionary fiscal policy), will result in recessionary effects. If you have an artificially high people will want to borrow lots of money (demand for loanable funds increases), however there is a. The demand for loanable funds will increase, interest rates will increase.